41 coupon collector problem in r
The Coupon-Collector Problem Revisited - Purdue University The Coupon-CollectorProblem Revisited Arnon Boneh and Micha Hofri Computer Sciences Department Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47907 CSD-TR-952 February, 1990 THE COUPON-COLLECTORPROBLEM REVISITED Amon Boneh- IOE Department, University ofMichigan, Ann Arbor MI 48109-2177 Micha Hofrit - Department ofComputer Science, The Technion-ITT,Haifa Collecting k Complete Sets of Coupons - MathPages with k=1 this is just the standard "collector's problem", which has a simple and well-known answer, namely, that the expected number of purchases is n (1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + ... + 1/n) this is analagous to a problem in reliability theory with n parallel redundant components, each with an exponential failure rate of 1/t, so the mean time to fail of …
Solved 5: Coupon collector's problem From Wikipedia, the - Chegg 5: Coupon collector's problem From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In probability theory, the coupon collector's problem describes "collect all coupons and win" contests. It asks the following question: If each box of a brand of cereals contains a coupon, and there are n different types of coupons, what is the probability that more ...

Coupon collector problem in r
(PDF) A note on the coupon - collector's problem with multiple arrivals ... Consider the classical coupon-collector's problem in which items of m distinct types arrive in sequence. An arriving item is installed in system i ≥ 1 if i is the smallest index such that system ... PDF 7. The Coupon Collector Problem - UNIVPM We will often interpret the sampling in terms of a coupon collector: each time the collector buys a certain product (bubble gum or Cracker Jack, for example) she receives a coupon (a baseball card or a toy, for example) which is equally likely to be any one of m types. Thus, in this setting, Xi∈D is the coupon type received on the ith ... R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem Raw coupon.R random.int <- function ( n) { sample.int ( n, 1) } random.coupon <- function ( ...) { count <- 0 have.coupon <- logical ( ...) while (! all ( have.coupon )) { have.coupon [random.int ( ... )] <- TRUE count <- count + 1 } count } sample.coupon <- function ( n, size=10*n) {
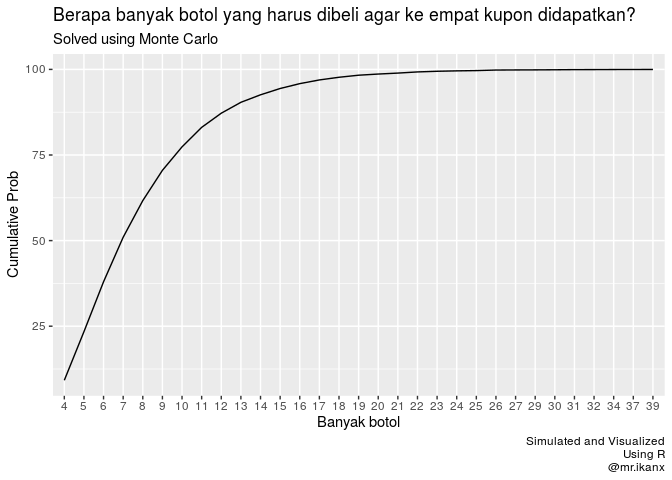
Coupon collector problem in r. Coupon collector's problem - Wikipedia The mathematical analysis of the problem reveals that the expected number of trials needed grows as . [a] For example, when n = 50 it takes about 225 [b] trials on average to collect all 50 coupons. Contents 1 Solution 1.1 Calculating the expectation 1.2 Calculating the variance 1.3 Tail estimates 2 Extensions and generalizations 3 See also 4 Notes PDF Collecting coupons — A mathematical approach - ed Asymptotics for the maximum in the coupon collector's problem. Math. Scientist, 27, 85-90. Wilkins, J. L. M. (1999). Cereal box problem revisited. School Science and Mathematics, 99(3), 193-195. 35 A u s t r a l i a n S e n i o r M a t h e m a t i c s J o u r n a l 2 0 (2) C o l l e c t i n g c o u p o n s ... Coupon Collecting Problem using Inclusion-Exclusion Coupon collector problem Incorrect recurrence solution. 0. Coupon collecting with unequal probabilities (S.Ross Min-Max approach) 1. Probability distribution in the subset version of the coupon collector's problem. 6. Modified coupon collector's problem, where you can trade off excess coupons. 10. coupon collector problem in R : AskProgramming I am new to programming and I am working with R at the moment to simulate the coupon collector's problem. Imagine there is a sticker album with 250 pictures. You can buy packs of 5 (those 5 in a pack are always different). The question is, how many packs does one have to buy, to complete the set.
Coupon Collector Problem Code - MathWorks for k = 1:coupon_num. if r == y (k) %checks if the random number is already in the vector y. else. y (r) = r; %if not adds the number to the vector in the position of the number. end. end. j = sum (y); %tracks to see if all the coupons have been selected. T (l) = T (l) + 1; %counts the number of times a selection has taken place. end. The Coupon Collector's Problem - YouTube Get 2 months of skillshare premium here! my discord server! coupon collector's problem goes as foll... The Weighted Coupon Collector's Problem and Applications Abstract In the classical coupon collector's problem n coupons are given. In every step one of the n coupons is drawn uniformly at random (with replacement) and the goal is to obtain a copy of all the coupons. It is a well-known fact that in expectation n \sum_ {k=1}^n 1/k \approx n \ln n steps are needed to obtain all coupons. Simulating the Coupon Collector's Problem - The DO Loop I want the simulation to work for the coupon collector's problem with K coupons, so I'll use a little probability theory. You can look up formulas for the mean and variance of the survival time as a function of K. For my simulation, I will use L = mean + 2*StdDev as the maximum number of rolls in each trial. When K =6, L is 41.
Help with Coupon Collector's Problem : R_Programming - reddit Hi, I'm struggling with a script in R to simulate the coupon collector's problem. Any help would be greatly appreciated! Here's the exercise: Write a function coupon (n) for simulating the coupon collector's problem. That is, let X be the number of draws required to obtain all n items when sampling with replacement. Coupon Collector Problem - Words and Mappings | Coursera It's a well known phenomenon that has lots of applications. And that's the combinatorics of the coupon collector problem. There is a combinatorial concept called a surjection that does really need analytic combinatorics to study. So what we call a coupon collector sequence is, it's an M-word with no empty set. So that's called an M-surjection. PDF Using Stirling numbers to solve coupon collector problems Marko R. Riedel March 13, 2019 The coupon collector problem has been studied in many variations, from ba-sic probability to advanced research. For an introduction consult the Wikipedia ... This was math.stackexchange.com problem 2426510. 2.1 Drawing coupons until at least 2 instances of each type PDF Math 365 Coupon Collector's Problem 1 Coupon Collector's ... - Amherst The objective of this lab is to study a famous problem in probability, the coupon collector's problem, and its connection to Poisson processes. 1 Coupon Collector's Problem: Geometric Distribution Approach A young baseball fan wants to collect a complete set of 262 baseball cards. The baseball cards are
Coupon Collector Problem - Words and Mappings | Coursera Coupon Collector Problem 13:45. Hash Tables 13:44. Mappings 23:23. Exercises 2:54. Impartido por: Robert Sedgewick. William O. Baker *39 Professor of Computer Science. Prueba el curso Gratis. Transcripción. Explora nuestro catálogo Inscríbete de manera gratuita y obtén recomendaciones personalizadas, actualizaciones y ofertas. ...
Coupon Collector Problem - Words and Mappings | Coursera Words and Mappings. We view strings as sets of characters or as functions from [1..N] to [1..M] to study classical occupancy problems and their application to fundamental hashing algorithms. Functions from [1..N] to [1..N] are mappings, which have an interesting and intricate structure that we can study with analytic combinatorics.
(PDF) Solution of the inverse coupon collector's problem The difference to the classical Coupon Collector is the response size which is 1 in the standard CC as opposed to the case of BT, where the response size is typically 50 or larger and can be...
Coupon Collector Problem | Brilliant Math & Science Wiki In the coupon collector problem, the goal is to purchase distinct objects in order to make a complete set of objects. Each purchase gives a random object, and the contents are independent of all other purchases. "Coupon" is just a placeholder word; the objects collected can be any kind of object. Mathematically, the goal of the problem is to quantify the effort required to complete the collection.
PDF Tighter bound for Coupon Collector using Union Bound Tighter bound for Coupon Collector using Union Bound Since the bounds that we obtain from Markov and Chebyshev for Coupon Collector are not "tight", we will now use the Union bound to get better results. Let Er i be the event that we have not yet obtained coupon ieven after rtrials. Then, Pr[Er i] = 1 1 n r e r n (1) We used the identity 1 + t ...
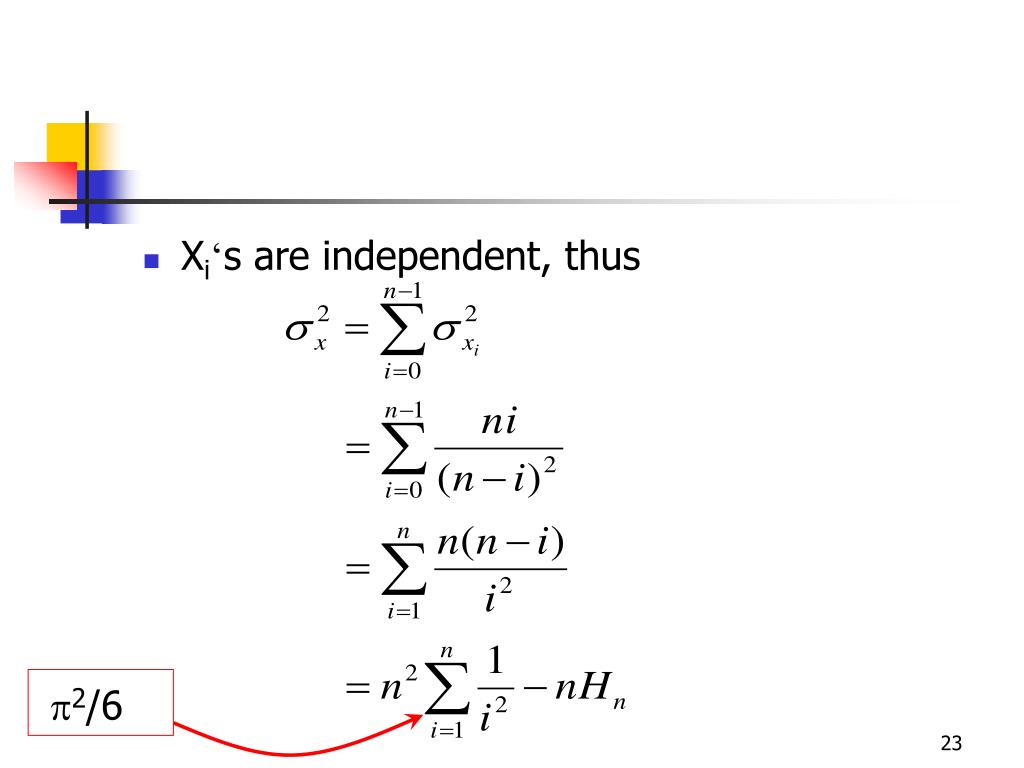
r-simulations/CouponCollector.md at master - GitHub actual_expectation_for_coupon_collector = function ( n) { # This is the E (X) for the coupon collector problem (1/n * (sum (1/j) for j from 1 to n)) n* (log ( n) + 0.577 ) } Results and Visualization Now that everything is in place, let's run some simulations and try to visualize them:
Expected Number of Trials until Success - GeeksforGeeks Coupon Collector Problem 1: Suppose there are n types of coupons in a lottery and each lot contains one coupon (with probability 1 = n each). How many lots have to be bought (in expectation) until we have at least one coupon of each type. The solution of this problem is also based on above result.
PDF MATerials MATemàtics 2 - Departament de Matemàtiques The history of the coupon collector's problem began in 1708, when the problemfirstappearedinDeMensuraSortis(OntheMeasurementofChance) written by A. De Moivre. More results, due among others to Laplace and Euler(see[8]foracomprehensiveintroductiononthistopic),wereobtained inthecaseofconstantprobabilities,i.e. whenp k 1 N foranyk.
PDF Lecture 6: Coupon Collector's problem The Coupon Collector's problem There are ndistinct coupons and at each trial a coupon is chosen uniformly at random, independently of previous trials. Let mthe number of trials. Goal: establish relationships between the number mof trials and the probability of having chosen each one of the ncoupons at least once. Note: the problem is similar ...
Coupon Collector's Problem - Amherst Coupon Collector's Problem Due Friday 3/11 (emailed pdf from Rmarkdown or handwritten on paper are both fine). The objective of this lab is to study a famous problem in probability, the coupon collector's problem, and its connection to Poisson processes. Coupon Collector's Problem: Geometric Distribution Approach
Inverse Coupon Collector's Problem - Rebecca's Home Page The Inverse Coupon Collector's Problem can be stated as follows: For fixed i, m, what value of N maximizes the probability p ( i, m; N )? That is, given i, m, what is the most likely value of N in...
R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem Raw coupon.R random.int <- function ( n) { sample.int ( n, 1) } random.coupon <- function ( ...) { count <- 0 have.coupon <- logical ( ...) while (! all ( have.coupon )) { have.coupon [random.int ( ... )] <- TRUE count <- count + 1 } count } sample.coupon <- function ( n, size=10*n) {
PDF 7. The Coupon Collector Problem - UNIVPM We will often interpret the sampling in terms of a coupon collector: each time the collector buys a certain product (bubble gum or Cracker Jack, for example) she receives a coupon (a baseball card or a toy, for example) which is equally likely to be any one of m types. Thus, in this setting, Xi∈D is the coupon type received on the ith ...
(PDF) A note on the coupon - collector's problem with multiple arrivals ... Consider the classical coupon-collector's problem in which items of m distinct types arrive in sequence. An arriving item is installed in system i ≥ 1 if i is the smallest index such that system ...











Post a Comment for "41 coupon collector problem in r"